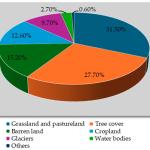
Purpose of the Attribution Section:
- Establishing Causality:
- It moves beyond simply documenting changes to determining the "why" behind them.
- It seeks to establish a causal link between human activities and observed climate trends.
- Informing Policy:
- Attribution is essential for informing policy decisions related to climate change mitigation.
- If human activities are the primary driver, then human actions are necessary to address the problem.
- Countering Skepticism:
- It provides scientific evidence to counter claims that climate change is solely due to natural variability.
Methods Used in Attribution Studies:
- Climate Models:
- Sophisticated computer models simulate the Earth's climate system, incorporating factors like greenhouse gas concentrations, solar radiation, and volcanic eruptions.
- Researchers run models with and without human-caused greenhouse gas emissions to compare the results.
- If the models accurately reproduce observed climate changes only when human factors are included, it strengthens the attribution argument.
- Statistical Analysis:
- Statistical techniques are used to analyze observed climate data and identify trends.
- Researchers look for patterns that cannot be explained by natural variability alone.
- They calculate the probability of observed changes occurring by chance versus being caused by human influence.
- Fingerprinting:
- This technique involves identifying unique "fingerprints" of different climate change drivers.
- For example, greenhouse gases have a distinct warming pattern in the atmosphere.
- By comparing observed warming patterns to these fingerprints, researchers can determine the relative contributions of different factors.
Expected Language and Findings:
- High Confidence:
- Expect very strong language expressing high confidence in the attribution of observed changes to human activities.
- Terms like "unequivocal," "extremely likely," and "virtually certain" are commonly used.
- Greenhouse Gases as the Primary Driver:
- The report will emphasize that the increase in greenhouse gas concentrations, particularly carbon dioxide, is the dominant factor driving global warming.
- The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes will be highlighted as the main sources of these emissions.
- Reduced Role of Natural Factors:
- Natural factors, such as solar variability and volcanic eruptions, will be shown to have a relatively small impact on recent climate changes.
- Natural variability will be discussed, but it will be shown that it cannot explain the current warming trend.
- Regional Attribution:
- Attribution studies may also focus on specific regions, assessing the human influence on regional climate changes, such as changes in precipitation or extreme weather events.
Importance of Strong Attribution:
- Policy Implications:
- Strong attribution provides a solid scientific basis for policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- It strengthens the argument for international cooperation and agreements.
- Public Understanding:
- Clear and compelling attribution helps to increase public understanding of the causes of climate change.
- It can help to build support for climate action.
In essence, the attribution section is where the science of climate change directly informs the need for societal action.